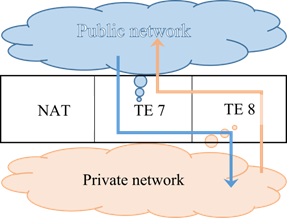
EcoNAT performs address translation, transferring data between the network interfaces that are combined into pairs. In each pair of network interfaces, one of them belonging to the private (local) side of the NAT, has an even number, and the other belonging to the public (global) of the NAT – has an odd number.
For example, the interface 8 is private (connected to the internal network), and the interface 7 – public (global addresses are placed on it).
The data that arrive at one of a pair of network interfaces, leaving NAT through another interface of the same pair (see figure below). If hairpinning is configured, data can leave the NAT through the same interface on which they arrived (see paragraph "Creating new pool").